The Big Data World

WHAT IS BIG DATA
Big data refers to the large, diverse sets of information that grow at ever-increasing rates. It encompasses the volume of information, the velocity or speed at which it is created and collected, and the variety or scope of the data points being covered.
Big data is a term that describes the large volume of data — both structured and unstructured — that inundates a business on a day-to-day basis. But it’s not the amount of data that’s important. It’s what organizations do with the data that matters. Big data can be analyzed for insights that lead to better decisions and strategic business moves.
THE NEED FOR BIG DATA
The term “big data” refers to data that is so large, fast, or complex that it’s difficult or impossible to process using traditional methods. The act of accessing and storing large amounts of information for analytics has been around a long time. The use of Big Data is becoming common these days by the companies to outperform their peers. In most industries, existing competitors and new entrants alike will use the strategies resulting from the analyzed data to compete, innovate and capture value.
Big Data helps the organization to create new growth opportunities and entirely new categories of companies that can combine and analyze industry data. These companies have ample information about the products and services, buyers and suppliers, consumer preferences that can be captured and analyzed. The importance of big data does not revolve around how much data a company has but how a company utilizes the collected data. Every company uses data in its own way; the more efficiently a company uses its data, the more potential it has to grow. The company can take data from any source and analyze it to find answers which will enable:

1.Cost Savings: Some tools of Big Data like Hadoop and Cloud-Based Analytics can bring cost advantages to business when large amounts of data are to be stored and these tools also help in identifying more efficient ways of doing business.
2.Time Reductions: The high speed of tools like Hadoop and in-memory analytics can easily identify new sources of data which helps businesses analyzing data immediately and make quick decisions based on the learnings.
3.Understand the market conditions: By analyzing big data you can get a better understanding of current market conditions. For example, by analyzing customers’ purchasing behaviors, a company can find out the products that are sold the most and produce products according to this trend. By this, it can get ahead of its competitors.
4.Control online reputation: Big data tools can do sentiment analysis. Therefore, you can get feedback about who is saying what about your company. If you want to monitor and improve the online presence of your business, then, big data tools can help in all this.
5.Boost Customer Acquisition and Retention: The customer is the most important asset any business depends on. There is no single business that can claim success without first having to establish a solid customer base. However, even with a customer base, a business cannot afford to disregard the high competition it faces. If a business is slow to learn what customers are looking for, then it is very easy to begin offering poor quality products. In the end, loss of clientele will result, and this creates an adverse overall effect on business success. The use of big data allows businesses to observe various customer-related patterns and trends. Observing customer behavior is important to trigger loyalty.
6.Solve Advertisers Problem and Offer Marketing Insights: Big data analytics can help change all business operations. This includes the ability to match customer expectations, changing the company’s product line, and of course ensuring that the marketing campaigns are powerful.
7.As a Driver of Innovations and Product Development: Another huge advantage of big data is the ability to help companies innovate and redevelop their products.
WHO USES BIG DATA
1)Banking:- Big data analytics can improve the extrapolative power of risk models used by banks and financial institutions. Big data can also be used in credit management to detect fraud signals and the same can be analyzed in real-time using artificial intelligence.
2)Education:- Big Data in the education sector would help improve student results, dropout rates at schools and colleges would also reduce. Educational institutions can use predictive analytics on all the data that is collected to give them insights on future student outcomes.
3)Government:- One of the core benefits of Big Data in governments has been eradicating fraud.
4)Health Care:- Improve care personalization and efficiency with comprehensive patient profiles. Identify geographic markets with a high potential for growth.
5)Manufacturing:- ERP, MES, CMMS, manufacturing analytics — there are many options, and when integrated via big data in manufacturing, patterns can be found, and problems can be solved
6)Retail:- Retail business like Amazon, Walmart, and many FMCG companies are using big data to understand customer behavior and build suitable offers for customers to increase their sales
TYPES OF BIG DATA

Structured Data
Structured data generally refers to data that has a defined length and format for big data.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner.
Semi-Structured Data
Semi-structured data is a form of structured data that does not conform with the formal structure of data models associated with relational databases or other forms of data tables, but nonetheless contain tags or other markers to separate semantic elements and enforce hierarchies of records and fields within the data.
THE 8V’s OF BIG DATA
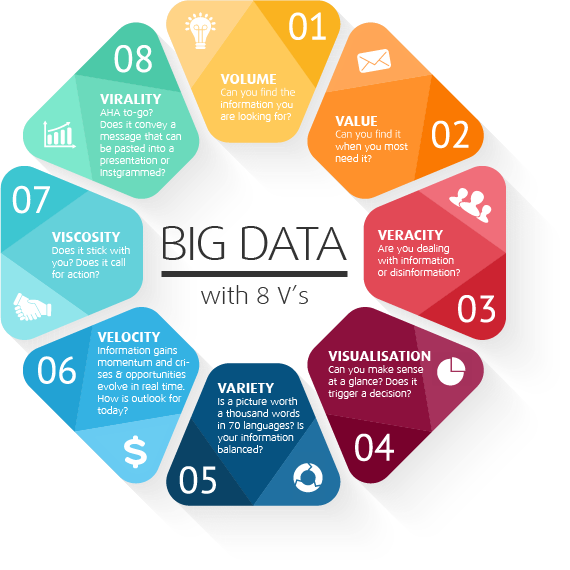
1. Volume:
When we talk about Big data, probably volume is the very first criteria for consideration. The range of volume justifies whether it should be considered as ‘big’ or not. Usually, if the volume of data is above gigabytes then only it is considered as big data from a volume perspective. What does measurement signifies here? It could be petabytes, terabytes, exabytes. This volume amount is considered based on data surveys of different organizations and here are some of the examples:
Also, this is actually the purpose of differentiating such enormous size of data as Big data from traditional structured data. In addition to that, RDBMS, or traditional database systems are not efficient to process or handle this data. Because it will take extended query time, cost, reliability, etc.
Also, as per IDC estimation by 2020, business transactions on the internet for B2B and B2C will reach 450 billion per day.
2. Velocity:
Stream analytics is a popular term today where high-speed data is processed using tools. But do you know stream analytics associated with which characteristics of big data? No doubt, it is the velocity of data. Here velocity means data generation speed, how frequently it is delivered and analyzed.
Now, the amount of data generated in today’s scenario is massive. Most importantly it needs real-time processing for analysis purposes. For example, Google alone generates more than 40k search queries per second. Hence, we can imagine how fast processing is required to get insights from data.
3. Variety:
Big data deals with any data formats — structured, unstructured, semi-structured, or even very complex structured. So, storing and processing unformatted data through RDBMS is not easy. However, such unstructured data provides more valuable insights on the information which we rarely get from structured data. Besides, a variety of data means different data sources. So, this characteristic of big data also provides information on the data sources.
4. Veracity:
Not that all data that come for processing are valuable. So, unless the data is cleansed correctly, it is not wise to store or process complete data. Especially when the volume is such massive. There comes this dimension of big data — veracity. These particular characteristics also helps to know whether the data is coming from a reliable source or it is the right fit for the analytic model.
5. Variability:
In Big data analysis data inconsistency is a common scenario that arises as the data is sourced from different sources. Besides, it contains different data types. Hence, to get meaningful data out of that enormous amount of data anomaly and outlier detection are essential. So, variability is considered as one of the characteristics of big data.
6. Value:
The primary interest for big data is probably for its business value. Perhaps this is the most crucial characteristic of big data. Because unless you get any business insights out of it, there is no meaning of other characteristics of big data.
7. Visualization:
Big data processing is not the only means of getting a meaningful result out of it. Unless it is represented or visualizes in a meaningful way, there is no point in analyzing it. Hence, big data must be visualized with appropriate tools which serve different parameters to help data scientists or analysts to understand it in a better way.
However, plotting billions of data points is not an easy task. Furthermore, it associates different techniques like using treemaps, network diagrams, cone trees, etc.
8. Validity:
Validity has some similarities with veracity. As the meaning of the word suggests, the validity of big data means how correct is the data for the purpose it is used for. Interestingly a considerable portion of big data remains un-useful which is considered as ‘dark data.‘ The remaining part of the collected unstructured data is cleansed first for analysis.
THE MASTER SLAVE ARCHITECTURE:
Master/slave is a model of asymmetric communication or control where one device or process (the “master”) controls one or more other devices or processes (the “slaves”) and serves as their communication hub.
Master: System where you are contributing or allocating your storage.
Slave: System who is actually giving the storage(Hard Disk).

This team of Master-Slave is referred to as “CLUSTER”…and the software which we use for Distributed Storage is- “HADOOP”.Apache HDFS or Hadoop Distributed File System is a block-structured file system where each file is divided into blocks of a pre-determined size. These blocks are stored across a cluster of one or several machines. Apache Hadoop HDFS Architecture follows a Master/Slave Architecture, where a cluster comprises of a single NameNode (Master node) and all the other nodes are DataNodes (slave nodes). HDFS can be deployed on a broad spectrum of machines that support Java.
NameNode is a very highly available server that manages the File System Namespace and controls access to files by clients. The HDFS architecture is built in such a way that the user data never resides on the NameNode. The data resides on DataNodes only.
DataNodes are the slave nodes in HDFS. Unlike NameNode, DataNode is a commodity hardware, that is, a non-expensive system which is not of high quality or high-availability.
ADVANTAGES OF BIG DATA
The following are the benefits or advantages of Big Data:
1.Big data analysis derives innovative solutions. Big data analysis helps in understanding and targeting customers. It helps in optimizing business processes.
2.It helps in improving science and research.
3.It improves healthcare and public health with the availability of records of patients.
4.It helps in financial tradings, sports, polling, security/law enforcement, etc.
5.Any one can access vast information via surveys and deliver answers to any query.
6.Every second additions are made.
7.One platform carry unlimited information.
DISADVANTAGES OF BIG DATA
The following are the drawbacks or disadvantages of Big Data:
1.Traditional storage can cost a lot of money to store big data.
2.Lots of big data is unstructured.
3.Big data analysis violates the principles of privacy.
4.It can be used for manipulation of customer records.
5.It may increase social stratification.
6.Big data analysis is not useful in the short run. It needs to be analyzed for a longer duration to leverage its benefits.
7.Big data analysis results are misleading sometimes.
8.Speedy updates in big data can mismatch real figures.
SOME CASE STUDIES OF BIG DATA IN COMPANIES :
1. Walmart

Walmart is the largest retailer in the world and the world’s largest company by revenue, with more than 2 million employees and 20000 stores in 28 countries. It started making use of big data analytics much before the word Big Data came into the picture.
Walmart uses Data Mining to discover patterns that can be used to provide product recommendations to the user, based on which products were brought together. Walmart by applying effective Data Mining has increased its conversion rate of customers. It has been speeding along big data analysis to provide best-in-class e-commerce technologies with a motive to deliver superior customer experience. The main objective of holding big data at Walmart is to optimize the shopping experience of customers when they are in a Walmart store. Big data solutions at Walmart are developed with the intent of redesigning global websites and building innovative applications to customize the shopping experience for customers whilst increasing logistics efficiency. Hadoop and NoSQL technologies are used to provide internal customers with access to real-time data collected from different sources and centralized for effective use.
2. Uber

Uber is the first choice for people around the world when they think of moving people and making deliveries. It uses the personal data of the user to closely monitor which features of the service are mostly used, to analyze usage patterns, and to determine where the services should be more focused. Uber focuses on the supply and demand of the services due to which the prices of the services provided change. Therefore one of Uber’s biggest uses of data is surge pricing. For instance, if you are running late for an appointment and you book a cab in a crowded place then you must be ready to pay twice the amount.
For example, On New Year’s Eve, the price for driving for one mile can go from 200 to 1000. In the short term, surge pricing affects the rate of demand, while long term use could be the key to retaining or losing customers. Machine learning algorithms are considered to determine where the demand is strong.
3. Netflix

It is the most loved American entertainment company specializing in online on-demand streaming video for its customers. Netflix has been determined to be able to predict what exactly its customers will enjoy watching with Big Data. As such, Big Data analytics is the fuel that fires the ‘recommendation engine’ designed to serve this purpose. More recently, Netflix started positioning itself as a content creator, not just a distribution method. Unsurprisingly, this strategy has been firmly driven by data. Netflix’s recommendation engines and new content decisions are fed by data points such as what titles customers watch, how often playback stopped, ratings are given, etc. The company’s data structure includes Hadoop, Hive, and Pig with much other traditional business intelligence.
Netflix shows us that knowing exactly what customers want is easy to understand if the companies just don’t go with the assumptions and make decisions based on Big Data.
4. eBay

A big technical challenge for eBay as a data-intensive business to exploit a system that can rapidly analyze and act on data as it arrives (streaming data). There are many rapidly evolving methods to support streaming data analysis. eBay is working with several tools including Apache Spark, Storm, Kafka. It allows the company’s data analysts to search for information tags that have been associated with the data (metadata) and make it consumable to as many people as possible with the right level of security and permissions (data governance). The company has been at the forefront of using big data solutions and actively contributes its knowledge back to the open-source community.
5. Procter & Gamble (P&G)

Procter & Gamble whose products we all use 2–3 times a day is a 179-year-old company. The genius company has recognized the potential of Big Data and put it to use in business units around the globe. P&G has put a strong emphasis on using big data to make better, smarter, real-time business decisions. The Global Business Services organization has developed tools, systems, and processes to provide managers with direct access to the latest data and advanced analytics. Therefore P&G being the oldest company, still holding a great share in the market despite having many emerging companies.
6. Facebook:
Arguably the world’s most popular social media network with more than two billion monthly active users worldwide, Facebook stores enormous amounts of user data, making it a massive data wonderland. Facebook is under the top 100 public companies in the world, with a market value of approximately $475 billion. Here I collect some details on which Facebook receives data on a daily basis.
- Users share 2.5 B Content every day.
- Users generate 2.7 B -Liked every day
- More than 250 billion photos have been uploaded to Facebook.
- 100+PB — Disk Space in a Single HDFS cluster.
- Hive is Facebook’s data warehouse, with 300 petabytes of data.
- 70,000 — queries executed
- 500+TB new data ingested
- Users spend an average of 20 minutes per day on the site.
- Facebook now sees 100 million hours of daily video watch time.
- 30% of internet users use Facebook more than once a day.
- Facebook generates 4 new petabytes of data per day.
7. Google
Google.com is the most visited website on our planet. Followed by YouTube.com. Both services are owned by Google. Besides these two there are other multiple online services owned by Google each with over a billion users like Gmail, Google Ads, Google Play, Google Maps, Google Drive, Google Chrome.
On a day to day basis, Google has to deal with petabytes of data. Just YouTube alone needs more than a petabyte of new storage every single day. Let alone the data storage requirements of all the services collectively. Google search receives approx. 5.4 billion searches every single day. By the year 2010, Google had over 10 billion images indexed in its database.
Google photo got pretty popular & has over 1.2 billion photos uploaded to the service every single day. Collectively the data amounts to approx. 14 petabytes of storage. The service has over a billion users.
YouTube is a social video sharing platform, the second most visited website on the planet. It has over a billion users. With over 2 billion users, the video-sharing platform is generating billions of views with over 1 billion hours of videos watched every single day. Here is a detailed article on the database and the backend infrastructure of YouTube.
Gmail & Google Drive have over 1.5 billion users. Google Play has over 1 billion users, it has had over 100 billion app downloads and approx. 3.5 million apps published. Google Maps has over 1 billion users. Google Analytics the website analytics service is the most widely used analytics service on the web. Google Assistant is installed on over 400 million devices. Google Chrome is the most used web browser in the world. Besides these, there are several other add on services offered by Google such as google docs, sheets, slides, calendars, etc. For a complete list of products offered by Google, here you go.
BIG DATA PREDICTING THE UNCERTAINTIES
A groundbreaking study in Bangladesh has found that using data from mobile phone networks to track movements of people across the country help predict where outbreaks of diseases such as malaria are likely to occur, enabling health authorities to take preventive measures.
Every year, malaria kills more than 400,000 people globally and most of them are children.
The different type of data, including information provided by the Bangladesh ministry of health, are used to create risk maps indicating the likely locations of malaria outbreaks so the local health authorities can then be warned to take preventative action, including spraying insecticides and stockpiling bed nets and medicines to protect the population from the disease.
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —